Traffic Cameras vs LiDAR Technology for Detection and Actuation
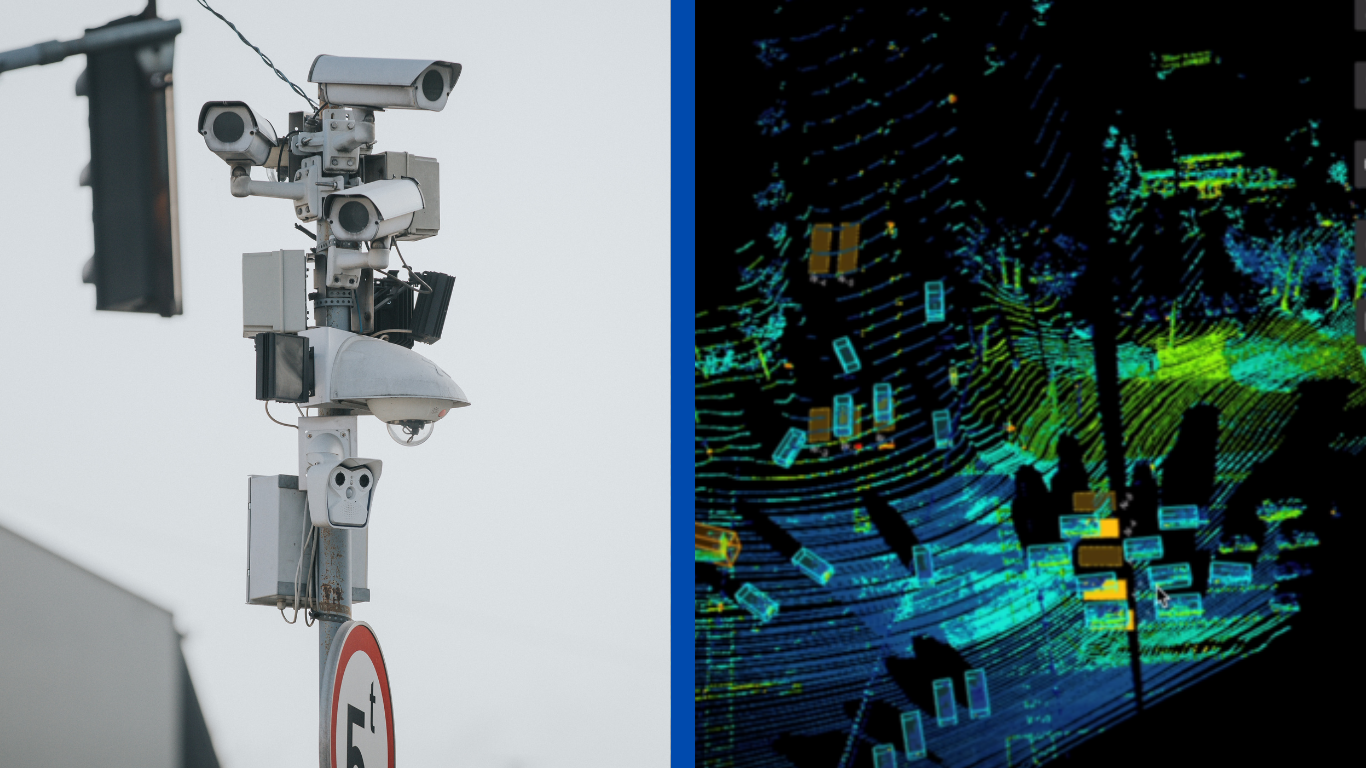

As cities around the world continue to grow, the demand for efficient traffic management solutions has never been greater. Traditionally, traffic signal cameras have been the go-to technology for monitoring and managing traffic flow. However, with the rise of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, the landscape of traffic detection and actuation is rapidly evolving.
LiDAR technology offers several advantages over traditional traffic signal cameras when it comes to traffic detection and management. Here’s why LiDAR can be the game-changer your city needs for optimal traffic detection and safety.
1. Precision & Accuracy
- LiDAR: LiDAR creates detailed 3D maps of the environment using laser pulses to generate point clouds, allowing for precise detection of objects, including their size, speed, and distance. This high level of accuracy enables better differentiation between various road users, such as cars, trucks, buses, cyclists, and pedestrians at an intersection.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: Traffic signal cameras provide 2D images or video footage that emulate 3D. Converting 2D footage into 3D environment requires unprecise calculations which can lead to lower accuracy in determining the exact position, size, or speed of objects. Their ability to detect and classify different road users is more limited compared to LiDAR.
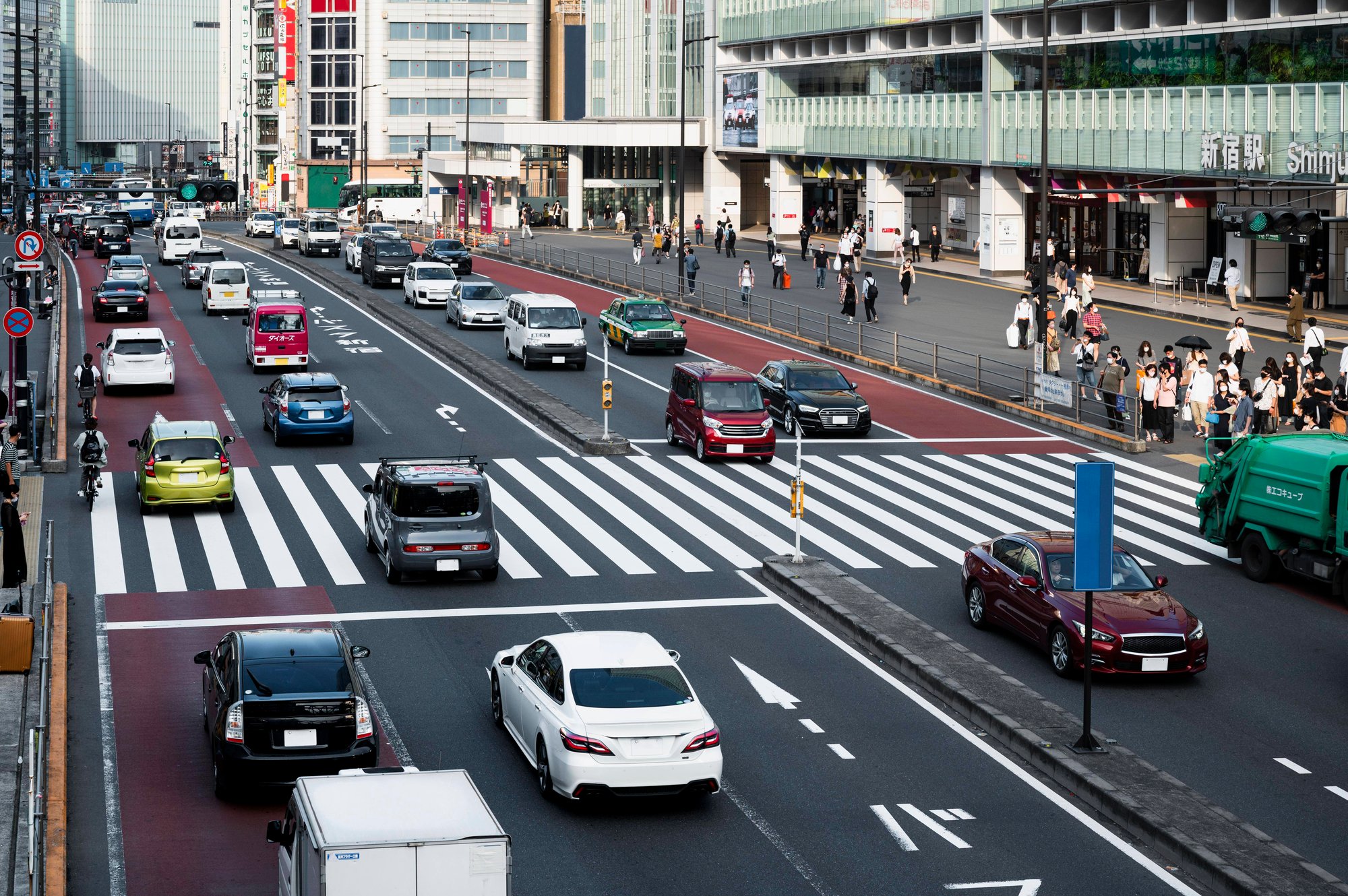

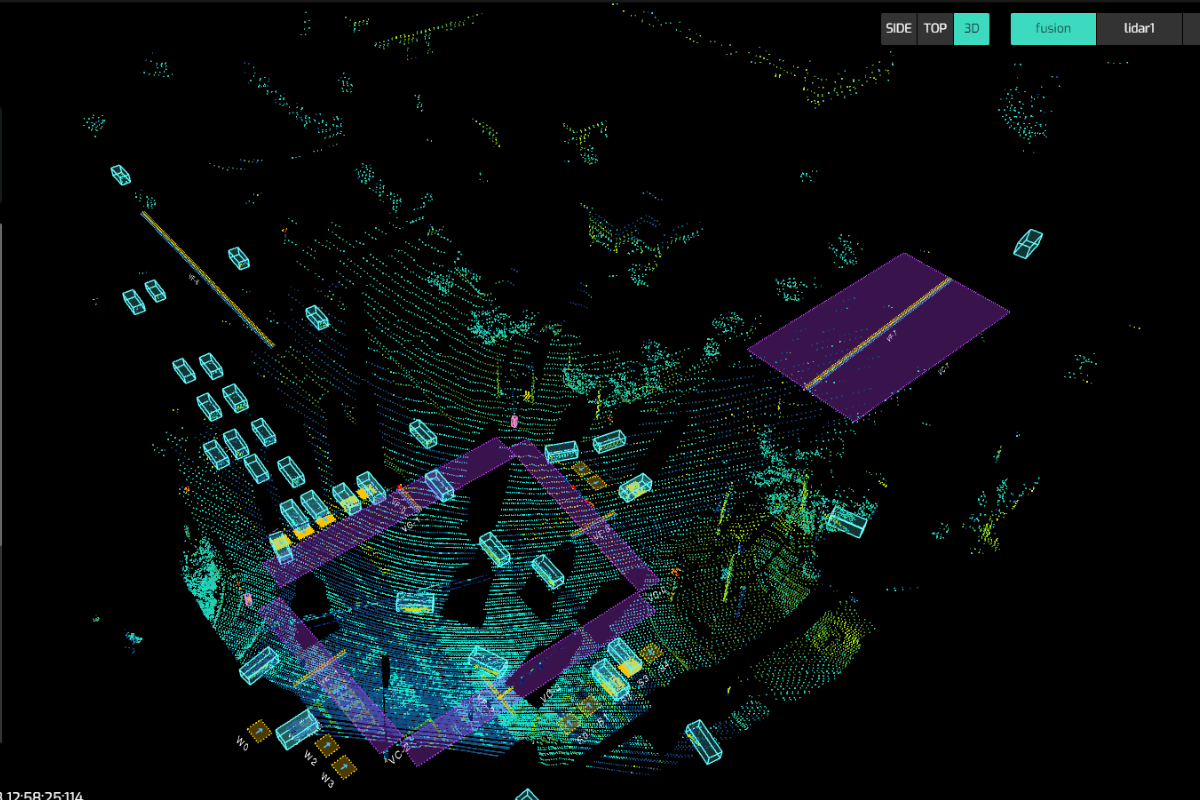
2. Reliability In All Weather and Lighting Conditions
- LiDAR: LiDAR is not affected by typical lighting conditions, meaning it works equally well during the day, at night, and in low-light situations under most circumstances. It can also perform effectively in various weather conditions, such as fog, rain, or snow.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: These cameras rely on visible light and can be hindered by poor lighting, glare, shadows, occlusion, or adverse weather conditions. This can reduce their effectiveness in certain situations, leading to less reliable detection. traffic engineering and operations practitioners
3. Privacy Concerns
- LiDAR: LiDAR does not capture personal identifiable images (PII) of people or vehicles, which makes it less intrusive in terms of privacy. It gathers data through laser reflections, ensuring privacy while still providing valuable traffic information. Unlike traditional systems, it does not collect or record biometrics data and does not use facial recognition.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: Cameras capture images and video, which can raise privacy concerns, especially in public spaces. While the data collected by cameras can be anonymized, there are still risks associated with the misuse of visual information. Due to legalities regarding privacy violations, some locations even rule out cameras as a form of traffic detection, particularly in Europe.
4. Object Detection and Classification
- LiDAR: LiDAR can classify different objects with a high degree of accuracy. It can distinguish between vulnerable and non-vulnerable road users, such as vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and more, providing comprehensive data for traffic management. LiDAR can be a valuable tool for applications such as volume/speed/occupancy/classification (VSOC) where roadside detection provides vehicle types that can be parsed on a per-lane usage basis.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: While cameras can detect and record objects at a similar accuracy rate to LiDAR, it is less reliable in most adverse weather and lighting conditions.
5. Field of view and coverage
- LiDAR: LiDAR systems typically offer between 120-degree and 360-degree field of view, allowing them to cover entire intersections or multiple lanes of traffic simultaneously. This wide coverage reduces the need for multiple sensors and simplifies the integration process.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: Traffic cameras generally have a limited field of view, often requiring multiple cameras to cover larger areas. While panoramic cameras can extend coverage, they still fall short of the comprehensive 3D mapping provided by LiDAR.
6. Real-Time Data and Analytics
- LiDAR: LiDAR systems can provide real-time data on traffic flow, road user behavior, and potential hazards. This data can be used to optimize traffic signal performance in response to changing driving patterns and behavior, enhance safety measures, and plan for future infrastructure needs.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: Cameras can also provide real-time data, but the processing of visual information can be slower and less accurate. Analyzing video footage often requires more computational resources, and it may not be as effective in generating actionable insights as LiDAR.
7. Low Maintenance
- LiDAR: Since LiDAR sensors are typically mounted on poles or other elevated structures, they are less susceptible to damage or wear and tear. This leads to lower maintenance costs and longer operational lifespans.
- Traffic Signal Cameras: Cameras can be prone to lens obstructions (e.g., dirt, snow) or physical damage, which may require more frequent maintenance and be more expensive to install.
In summary
When it comes to traffic detection and actuation, both LiDAR and traffic cameras have their merits. However, LiDAR technology offers superior 3D precision, reliability, and data-gathering capabilities as compared to traditional traffic signal cameras. Its ability to function effectively in all weather conditions, classify various road users, and protect privacy makes it a more advance and future-proof solution for traffic detection and actuation.
THE FUTURE OF URBAN TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT: USING LiDAR and AI for Smarter Cities
Download our white paper on how advance technologies are revolutionizing traffic systems for safer, smarter urban environments.
